What is GA4?
GA4 is built on the Google analytics app + web application backbone (Firebase). In data collection and reporting, GA4 takes a different approach from what you used to see in Universal Analytics (UA).
Through transitioning to an ‘event’-based model, Google is pushing advertisers to reconsider how they view user data. In GA4, knowledge is gathered and interpreted differently, as it focuses mainly on the activities and experiences of the user’s journey.
It is important to identify that this will become the latest Google Analytics default, as new Google Analytics configurations usually enable you to set up GA4 and44, not UA. Fortunately, we can run GA4 parallel with the current UA setup to show you how to set this up.
New setups for UA Property are still available. After clicking ‘Create Land,’ look for the link ‘Display Advanced Options.’ You will have the option to create GA4 and UA or create UA only.
How to Set Up GA4: Step By Step Process
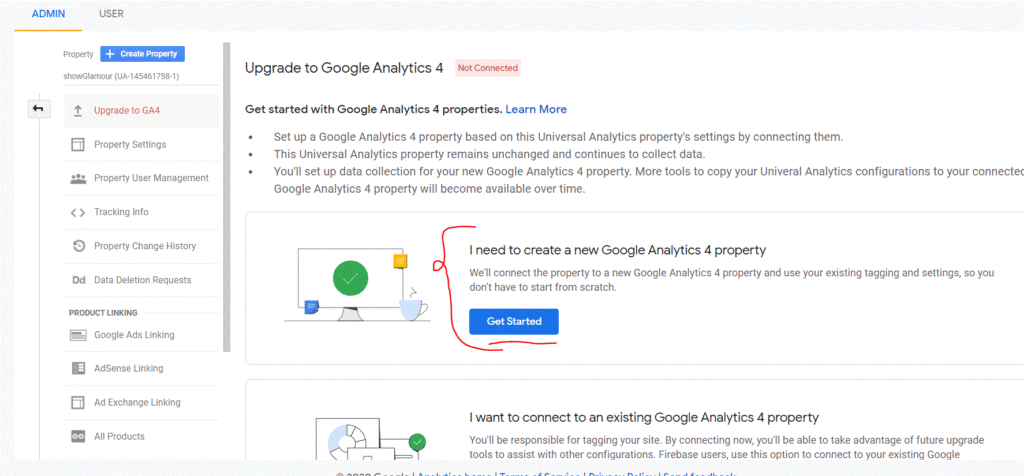
- Let’s get started by navigating inside your Google Analytics account to your Admin Settings. Look for the Upgrade to Google Analytics 4 Property link under Property Settings.


If you do not have an upgrade option available, you can click ‘Create Property‘ to create a new GA4 Property and skip to step 4 after setting up Create Property.
2. To begin the setup process with the Google Analytics setup wizard, click ‘Get Started.’ Then, depending on your current Google Analytics 4 you will have many choices.

If you use Google Site Tag to enforce UA, the wizard will allow your existing tags to collect data.
- You’ll need to create a measurement ID for your new GA4 property to start data collection. The Measurement ID is identical to the UA ID. By clicking the right arrow shown below, enter the ‘Tag installation’ menu.
2. GA4 has no views like its predecessor’s. It has Data Streams instead. As it automatically tracks such events such as Scrolls, Outbound Connection Clicks, Site Search, File Downloads, and more, the Data Stream extends beyond the Pageview Request. Expand the Add Stream drop-down and choose the app that you want to track.
3. Set up your data source by entering the URL of your website and the name of the stream. When done, press ‘Create Stream.’
4. You have your Measurement ID now. Copy or take note of the Measurement ID as needed in Google Tag Manager to set up the GA4 Configuration Tag.
5. Navigate to your Google Tag Manager Dashboard, create a new tag, select ‘Tag Configuration’ and choose ‘Google Analytics: GA4 Settings’ as the tag type.
6. Next, add the Measurement ID. Instead of entering it manually, it is suggested to create a Constant Variable for the Measurement ID. It will allow you to reference and avoid future inconsistencies with the Measurement ID for other tags.
7. To create a Constant Variable, complete the steps below:
- Tap on the Variable icon
- Creating a new Variable
- To fill in the Variable Type list, press Variable Configuration.
- Under Utilities, pick the ‘Constant’ Variable
- In the Value field, enter your GA4 Measurement ID and hit Save
8. Configure your trigger to fire on pages now that the Tag is set, and click Save to complete the GA4 setup.
9. You can use Tag Manager’s Preview Mode to test your GA4 Tag, or you can publish your container to push the new Tag live. After checking, remember to publish your container; otherwise, your GA4 property will not receive data. You can view live hits by visiting the GA4 Realtime report once the Tag is live. The published Tag can also be viewed in Google Tag Assistant. You can start using it to track users and their actions more efficiently now that you’ve set up GA4.
Wrapping Up:
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) tool allows a unified measurement between your website and app of user interactions and events. You can use GA4 Properties for your Google Analytics measurement strategy if your mobile app includes embedded web views, a similar web app, or web pages that mimic or otherwise expand the mobile experience.
Recommended Reads from Author:












Leave a Reply